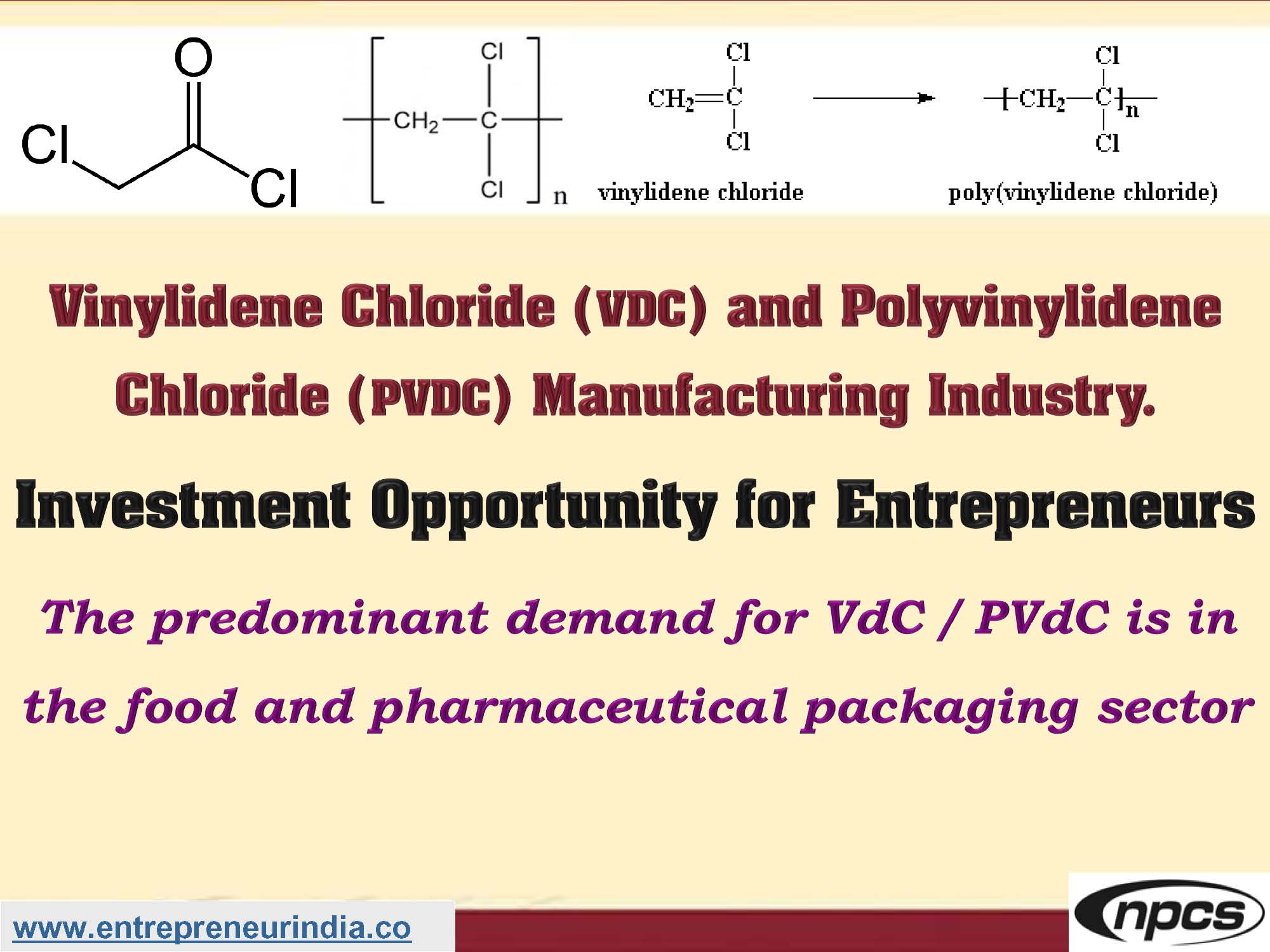
The Vinylidene Chloride and Polyvinylidene Chloride manufacturing industry plays a significant role in the global polymer and packaging sectors. Known for their superior barrier properties, these polymers are critical in food packaging, industrial films, coatings, and flame-retardant materials. With increasing demand for high-performance, lightweight, and flexible packaging materials, Vinylidene Chloride (VDC) and its polymer Polyvinylidene Chloride (PVDC) continue to gain momentum in industrial applications.
Market Demand and Industrial Importance
The demand for Vinylidene Chloride and Polyvinylidene Chloride has increased due to their exceptional resistance to oxygen, moisture, chemicals, and vapor. These materials are highly valued in multilayer food packaging to prolong shelf life. PVDC coatings also find usage in pharmaceutical blister packs, waterproof coatings, and barrier films. The industry caters to major downstream markets including FMCG, healthcare, agriculture, and electronics.
Key Applications of Vinylidene Chloride and PVDC
The exceptional chemical structure of VDC and PVDC provides versatile application benefits:
-
Food Packaging Films: Used for vacuum-sealed and heat-shrinkable packaging for meat, cheese, and snacks
-
Pharmaceutical Packaging: PVDC is applied as a barrier coating on blister packs to protect drugs from moisture
-
Coatings and Adhesives: Offers chemical resistance and adhesion for aluminum, paper, and plastic laminates
-
Flame-Retardant Textiles: PVDC is added to textiles to improve fire resistance and reduce smoke emission
-
Agricultural Films: Offers UV-resistance and durability for greenhouse coverings
-
Electronics and Batteries: Used in insulation films, sensor protection, and flexible electronics
The polymers’ durability and flexibility make them indispensable in advanced manufacturing industries.
Raw Materials Required
The production of Vinylidene Chloride and Polyvinylidene Chloride involves several chemical precursors:
-
Ethylene Dichloride (EDC)
-
Chlorine Gas
-
Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM)
-
Catalysts (Ferric Chloride, Organic Peroxides)
-
Solvents (for purification)
-
Deionized Water
-
Polymerization Inhibitors (as needed)
Sourcing high-purity raw materials ensures safety, better yield, and consistent product quality.
Manufacturing Process of Vinylidene Chloride
The production of VDC begins with chlorination:
-
Chlorination of Ethylene
Ethylene reacts with chlorine to form 1,2-dichloroethane (EDC) in a chlorination reactor. -
Thermal Cracking of EDC
EDC undergoes thermal cracking in a furnace to produce Vinyl Chloride Monomer (VCM). -
Chlorination of VCM to VDC
VCM reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst (FeCl? or CuCl?) at moderate temperature and pressure to form Vinylidene Chloride. -
Purification
Unreacted chlorine and by-products are separated using distillation and scrubber systems. VDC is condensed and stored in pressurized tanks.
Proper temperature control, safety systems, and emission management are crucial at every stage.
Polymerization Process for PVDC
Polyvinylidene Chloride is manufactured through suspension or emulsion polymerization:
-
Initiation
VDC monomers are added to a polymerization reactor with water, stabilizers, and emulsifiers. Free radical initiators are introduced. -
Polymer Growth
Polymer chains form and grow as monomers convert into long chains of PVDC under controlled agitation and temperature. -
Recovery
The polymer is separated from the liquid phase through filtration and then dried using rotary dryers. -
Pelletizing and Packaging
The dry PVDC is pelletized and packed in airtight containers to prevent contamination and moisture absorption.
Suspension polymerization produces coarse, free-flowing granules, while emulsion polymerization yields fine particles used in coatings.
Plant Infrastructure and Machinery Required
To set up a Vinylidene Chloride and PVDC manufacturing plant, invest in:
-
Reactor vessels (lined for corrosion resistance)
-
Distillation Columns and Condensers
-
Polymerization Reactors with Agitators
-
Dryers (Rotary or Tray Type)
-
Pelletizers and Sievers
-
Fume Extraction and Scrubber Systems
-
Fireproof Storage Tanks and Solvent Handling Units
Automation systems with DCS or PLC integration improve safety and batch accuracy.
Safety, Environmental, and Regulatory Compliance
Due to the toxic and flammable nature of VDC, safety is non-negotiable:
-
Use closed-loop systems to prevent VDC vapor emissions
-
Install scrubbers and activated carbon filters to treat off-gases
-
Implement leak detection and neutralization systems
-
Provide flame-proof storage and anti-static equipment
-
Train staff for emergency handling and evacuation drills
Regulatory clearances required include:
-
Pollution Control Board Approval
-
Explosive Storage License (for VDC)
-
Factory License and Fire NOC
-
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
-
Hazardous Waste Management Authorization
-
REACH and RoHS compliance for export
Market Potential and Global Opportunities
The global PVDC market is project to grow due to the rise in:
-
Packaged food consumption
-
Pharmaceutical exports
-
Flexible electronics demand
-
Sustainable multilayer packaging
-
Lightweight barrier films
Major buyers include FMCG giants, pharmaceutical firms, and electronic packaging suppliers. Export opportunities exist in USA, Europe, Japan, and Middle East markets where stringent quality standards are require.
Cost Analysis and Profitability
Setting up a medium-scale VDC and PVDC plant (5–10 tons/day) may require ?50–?120 crores, depending on capacity and automation. Operating costs are offset by:
-
High-margin specialized polymers
-
Steady B2B contracts
-
Import substitution advantages
-
Premium pricing for moisture-sensitive packaging films
With consistent demand and limited competition, gross margins can range between 20% to 30%, with ROI achievable in 4–5 years.
Licensing and Certifications
Ensure all certifications are secure:
-
MSME/Udyam Registration
-
GST and IEC Codes
-
ISO 9001, ISO 14001
-
BIS Compliance for Polymer Quality
-
REACH Certification for European Markets
-
FDA Certification for Pharmaceutical-grade Applications
Strong documentation improves brand credibility and allows entry into regulated industries.
Conclusion
The Vinylidene Chloride and Polyvinylidene Chloride manufacturing industry offers strong profitability, sustained global demand, and diversified applications across critical industries. With proper compliance, investment in high-quality infrastructure, and adherence to safety norms, entrepreneurs can create a robust chemical manufacturing enterprise. These polymers will continue to dominate barrier packaging and performance coatings, ensuring long-term market relevance and financial returns.
Niir Project Consultancy Services
An ISO 9001:2015 Company
106-E, Kamla Nagar, Opp. Spark Mall,
New Delhi-110007, India.
Email: npcs.ei@gmail.com , info@entrepreneurindia.co
Tel: +91-11-23843955, 23845654, 23845886, 8800733955
Mobile: +91-9811043595
Website: www.entrepreneurindia.co , www.niir.org





